Tree DFS 순회
나랑 비슷한 사람과 대화를 했다. 입문하고 처음 내가 했던 생각, 내가 가졌던 사고, 내가 했던 행동, 재훈이처럼 말해줬다. 보고싶다 재훈아..
이전 피보나치 수열 이후로 그냥 수월하게 풀어진 문제. DFS는 모르겠고 그냥 객체내 배열이 있는걸 1차원 배열로 나열했다. 그러니까 되네?
0. q
임의 트리 node 중 한개의 Node 객체를 입력받아, 해당 node를 시작하여 Depth Fist Search를 한다. 탐색되는 순서대로 node의 값이 저장된 배열을 리턴한다.(한국말은 어렵다)
1. i
- parameter: Node = { value: number, children: [Node1, Node2…] }
2. o
- array
3. c
Node, addChild 변경 금지
4. io ex
let head = new Node(1);
let eye = head.addChild(new Node(2));
let nose = head.addChild(new Node(3));
let lEyeball = eye.addChild(new Node(4));
let rEyeball = eye.addChild(new Node(5));
let output = dfs(root);
console.log(output); // --> [1, 2, 4, 5, 3]
/**
* 1
* 2 3
* 4 5
*
* 순차적으로 순회하면 될거같음
*/
leaf1.addChild(new Node(6));
rootChild2.addChild(new Node(7));
output = dfs(root);
console.log(output); // --> [1, 2, 4, 6, 5, 3, 7]
/**
* 1
* 2 3
* 4 5 7
* 6
*
* 풀때는 몰랐네 그려보니 이해가 더 쉬움
*/
5. static
// 이 아래 코드는 변경하지 않아도 됩니다. 자유롭게 참고하세요.
let Node = function (value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = [];
};
// 위 Node 객체로 구성되는 트리는 매우 단순한 형태의 트리입니다.
// membership check(중복 확인)를 따로 하지 않습니다.
Node.prototype.addChild = function (child) {
this.children.push(child);
return child;
};
6. mine
//인자 하나 더 늘려서 편하게감.
let dfs = function (node, resultArr) {
//객체내 value 꺼내고, children 빈배열인지 확인 그다음으로
//처음일때 생성
if (resultArr === undefined) resultArr = [];
//일단 value 넣고
resultArr.push(node.value);
//console 찍었더니 undefined는 없고 빈배열은 무조건 있음
//빈배열이면 다음으로 넘어감
for (node of node.children) {
dfs(node, resultArr);
}
//끝나면 반환
return resultArr;
};
7. reference
이렇게도 1차원배열로 붙는다고???
let dfs = function (node) {
//value 배열
let values = [node.value];
//foreach로 순회, concat으로 재귀
node.children.forEach((n) => {
values = values.concat(dfs(n));
});
return values;
};
8. 재귀를 사용한 트리의 DFS 순회 from geeksforgeeks.org
이진 트리ㅡ 재귀를 사용해 깊이 우선 탐색을 사용하여 순회한다.
선형 데이터구조(Array, Linked List, Queues, Stacks 등)는 순회법이 논리적 방법이 하나이나 트리는 다양하다(2차원이라며 ㅡㅡ)
- DFS
- BFS(너비 우선 순회)
8-1. DFS
트리 또는 그래프를 탐색할때 사용한다. 역추적은 순회에 사용한다. 가장 깊은 노드를 방문한 다음 해당 노드의 형제가 존재하지 않는 경우 상위 노드로 역추적한다.(문제랑은 다르지만 이것도 재밋겠는걸) 트리의 DFS는 “비교적”쉽다.(어쩐지) 다음 순환에 신경쓰지 않고 인접을 순회하면 된다. 단일 노드(root)에서 시작하여 끊김없이 전체 트리를 탐색하는 것이 보장된다.
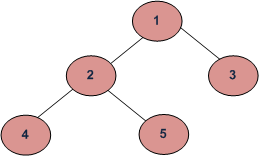
- Inorder(Left, Root, Right): 4-2-5-1-3
- Preorder(Root, Left, Right): 1-2-4-5-3 (문제)
- Postorder(Left, Right, Root): 4-5-2-3-1 (넓이탐색인가?)
8-1-1. Inorder
Algorithm Inorder(tree)
- 왼쪽 하위 트리를 탐색합니다. 즉, Inorder(left-subtree)를 호출합니다.
- 루트를 방문하십시오.
- 오른쪽 하위 트리를 탐색합니다. 즉, Inorder(right-subtree)를 호출합니다.
// javascript program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.key = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder */
function printInorder(node) {
if (node == null) return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
document.write(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// Driver method
var root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("<br/>Inorder traversal of binary tree is <br/>");
printInorder(root);
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
- output: 4-2-5-1-3
- 용도: 이진 탐색 트리(BST) 감소하지 않는 순서로 노드를 제공한다. 증가하지 안흔 순서로 BST의 노드를 얻으려면 Inorder traversal이 반전되는 변형을 사용할 수 있다.
8-1-2. Preorder
Algorithm Preorder
- 루트를 방문하십시오.
- 왼쪽 하위 트리를 탐색합니다. 즉, Preorder(left-subtree)를 호출합니다.
- 오른쪽 하위 트리를 탐색합니다. 즉, Preorder(right-subtree)를 호출합니다.
// JavaScript implementation of above approach
// A class that represents an individual node in a
// Binary Tree
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.val = key;
}
}
// A function to do preorder tree traversal
function printPreorder(root) {
if (root) {
// First print the data of node
document.write(root.val, " ");
// Then recur on left child
printPreorder(root.left);
// Finally recur on right child
printPreorder(root.right);
}
}
// Driver code
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Preorder traversal of binary tree is", "</br>");
printPreorder(root);
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
- output: 1-2-4-5-3
- 용도: 트리의 복사본을 만드는데 사용된다. Preorder traversal의 표현식 트리에서 접두사 표현식을 가져오는데도 사용된다. 접두사 표현식이 유용한 이유는 위키를 참조.
8-1-3. Postorder
Algorithm Postorder
- 왼쪽 하위 트리를 탐색합니다. 즉, Postorder(left-subtree)를 호출합니다.
- 오른쪽 하위 트리를 탐색합니다. 즉, Postorder(right-subtree)를 호출합니다.
- 루트를 방문하십시오.
// javascript program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
constructor(item) {
this.key = item;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
var root;
/*
* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the "bottom-up" postorder
* traversal.
*/
function printPostorder(node) {
if (node == null) return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
document.write(node.key + " ");
}
// Driver method
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is<br/> ");
printPostorder(root);
// This code contributed by umadevi9616
- output: 4-5-2-3-1
- 용도: Postorder순회는 트리를 삭제하는데 사용된다. 트리삭제 참조. 후위순회는 표현식 트리의 후위 표현식을 얻는데도 유용하다.
8-1-4. DFS를 사용하여 모든 순회 구현
// JavaScript program to for tree traversals
// A class that represents an individual node in a
// Binary Tree
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.val = key;
}
}
// A function to do inorder tree traversal
function printInorder(root) {
if (root) {
// First recur on left child
printInorder(root.left);
// then print the data of node
document.write(root.val, " ");
// now recur on right child
printInorder(root.right);
}
}
// A function to do postorder tree traversal
function printPostorder(root) {
if (root) {
// First recur on left child
printPostorder(root.left);
// the recur on right child
printPostorder(root.right);
// now print the data of node
document.write(root.val, " ");
}
}
// A function to do preorder tree traversal
function printPreorder(root) {
if (root) {
// First print the data of node
document.write(root.val, " ");
// Then recur on left child
printPreorder(root.left);
// Finally recur on right child
printPreorder(root.right);
}
}
// Driver code
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Preorder traversal of binary tree is", "</br>");
printPreorder(root);
document.write("</br>", "Inorder traversal of binary tree is", "</br>");
printInorder(root);
document.write("</br>", "Postorder traversal of binary tree is", "</br>");
printPostorder(root);
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
- output:
- preorder 1 2 4 5 3
- inorder 4 2 5 1 3
- postorder 4 5 2 3 1
- bigO
- 시간 복잡도: 0(n)
- 보조공간: 함수 호출을 위한 스택 크기를 고려하지 않으면 0(1), 아니면 0(n)
참조
geeksforgeeks: dfs-tree
gfgs: level order tree
wiki: polish notation
gfgs: delete tree